Frequentyl Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Equality and Discrimination
-
Discrimination in the Work Place
- What does gender discrimination at the work place mean?
- What time is likely to be discriminated the workplace?
- Who may be discriminating at the workplace?
- What are the types of discrimination in the hiring process?
- What is discrimination in employment?
- What forms of discrimination can be identified during the dismissal and / or refusal to renew your contract?
- The Rights of the Labor Process
Equality and Discrimination
What is Gender?
Sex has two categories: biological (sex) and social (gender). “Sex” is related to the physical, anatomical difference between men and women, while the notion of "gender" refers to the psychological, social and cultural roles. Sex is biologically determined, gender is determined by social and cultural factors and defines combination of the socially learned behaviors, characteristics and attitudes of men and women.
What is the gender stereotypes?
Gender stereotypes are formed on the basis of gender roles. This is the combination of the ideas, opinions, prejudices that are considered typical for men or women in a given society at a given historical period. For example, "men are more aggressive", "men are smarter", "women are more emotional", "women cannot drive well." Such stereotyped roles give men more possibility to reach the dominance in the society, however, they are less involved in raising of their own children. Gender inequality and gender stereotypes are directly related to each other. To certain extent gender stereotypes is the methodology of sexism and unequal division of labor is based on it.
What is sexism?
Sexism is a discrimination of a person or a group of persons based on sex or gender. It includes those social stereotypes, beliefs and ideas which establish the dominance of one sex over another and forms the basis of gender inequality. Racism and sexism are similar by their ideological functions.
Absolutizing and biologizing gender differences created based on social conditions and cultural norms constitutes the source of sexism. Male dominance is deemed normal by sexism. This ideology that is revealed in the violations of human rights humiliates and puts women at disadvantage.
Base on the definition of sexism, gender discrimination applies to men as well as women. However, due to the fact that the majority of the world’s cultures is patriarchal, the women become the victims of sexism more often.
What is gender equality?
Gender equality is one of the essential characteristics of the society based on social justice principle and is the part of human rights. Gender equality means that women and men have equal conditions and life chances for the full realization of their potential, are equally involved in the political, economic, social, cultural development and equally enjoy the benefits, opportunities and resources. Gender equality does not mean women and men are identical, on the contrary – it is recognized in the society that people have different values and goals, different needs and lifestyle, however, their interests should equally be taken into account at all levels, they should enjoy equal rights and opportunities and have equal responsibilities and obligations in all areas of social life.
Emphasizing differences between men and women takes place differently in different cultures, however, in the states where the level of economy is high and the state governance is based on democratic, liberal approach, the above difference is not in fact noticeable. The approach of the modern society is based on the reduction of difference between sexes and on elimination of one sex’s dominance over another. It is scientifically proven that both sexes are equally able to combine wide spectrum of each other's activities, skills and behaviors.
What is temporary special measures?
Temporary special measures i.e. positive discrimination is the set of temporary measures, the necessary structural, social and cultural changes, which are aimed to achieve gender equality and elimination of all forms of discrimination based on sex.
What is gender mainstreaming?
Gender mainstreaming constitutes the concept that implies inclusion of gender issues at all levels and all stages of policy directions. The European Commission defines it as a “strategic long-term approach, which introduces gender equality in systems, structures, institutions, programs, policies and practices
What is discrimination?
Discrimination (Lat. Discrimination, difference) means - inequality, unfair treatment or preference to people based on race, ethnic origin, colour, sex, religion, sexual orientation, gender identity and other grounds.
Discrimination can be "de jure" (i.e., legal), which is provided by the current legislation and "de facto", when the dominant group is having advantages over the minorities.
Discrimination can be direct or indirect. Direct discrimination is the kind of treatment or creating the conditions when one person is treated less favourably than another person in a comparable situation on any grounds. Indirect discrimination is a situation where a provision, criterion or practice, neutral in form but discriminatory in substance, puts persons at a disadvantage compared with another persons in a comparable situation
What is gender discrimination?
Gender discrimination means any kind of different treatment, exclusion and / or limitation based on sex, , which is reflected in the recognition of different rights and fundamental freedoms, equal opportunities in programs, or by lowering or fully rejecting them.
Discrimination in the Work Place
What does gender discrimination at the work place mean?
Gender discrimination at the workplace means the kind of treatment or creation of the conditions when one person is treated less favourably than another person in a comparable situation on any grounds or when persons in inherently unequal conditions are treated equally in the enjoyment of the rights provided for by the legislation of Georgia.
What time is likely to be discriminated the workplace?
Workplace discrimination occurs during:
• hiring process
• Working process
• Dismissal
Who may be discriminating at the workplace?
Discrimination at the workplace can be committed by:
• manager, head, coordinator;
• Can occur between employees;
• By a third party (client, customer, partner)
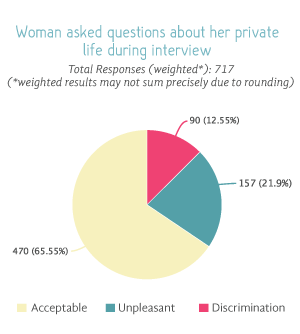
What are the types of discrimination in the hiring process?
Discrimination during the hiring discrimination may be identified if:
• during the interview the employer asks questions regarding:
A) Marital status:
B) Your plans for marriage;
C) Number of children;
D) Whether you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
• If during the job interview the employer expresses a clear preference to the person of the opposite sex.
What is discrimination in employment?
Discrimination during the working process may be identified if:
• Your salary is lower than the salary of an opposite sex colleague who is working on the same position and has the same qualifications as you;
• The employer does not give you or gives you less paid/unpaid leave or bonuses than to the opposite sex colleague with a similar position as you;
If you don’t have the opportunity to take part, or are given less opportunity to improve your qualifications through trainings and seminars
If you don’t have any possibility of advancement and promotion;
If your employer asks you more than the other employees to work overtime (weekends, Saturday - Sunday, late in the evening);
If the employer has not given you a maternity and child care leave and / or time required for the medical examinations and / or breastfeeding and / or additional parental leave;
If you become a victim of sexual harassment at the workplace (when there are inappropriate comments on your appearance, unfavourable comments about your personal life, talking to you during free time on matters that are of a sexual nature, personal letters, messages, emails, intimate touching; offers or / and forced sex);
• If you are regularly asked to complete the tasks that are not within the scope of your job description, just because you are a woman / man;
• If your opinion is systematically ignored, just because you are a woman / man
What forms of discrimination can be identified during the dismissal and / or refusal to renew your contract?
• If you are dismissed and / or employment contract is not renewed:
A) During pregnancy;
B) During the maternity leave;
B) Right after the end of maternity leave;
D) Due to the absence because of child care;
• If the employer prefers the employer of the opposite-sex;
• If you refused an offer of a sexual nature and / or did not complete the tasks that are not within the scope of your job description;
• If the employer dismissed you because of pregnancy;
• If your employer found out that you have under age children.
-
Discrimination may also occur in other cases too- when you are working at the site and are treated in different (unequal) manner.
The Rights of the Labor Process
When are you entitled to paid/unpaid leave?
According to the Labor Code, the employee is entitled to a paid leave of at least 24 working days; and an unpaid leave of at least 15-days. (Article 21)
An employee shall have the right to request leave after working for 11 months. By agreement of the parties, the employee may be granted leave even before the said term elapses. By agreement of the parties, a leave may be used in parts.
What is maternity leave?
Maternity leave is a leave received during the pregnancy or child care. According to the Georgian Labor Code – An employee, at his/her own request, shall be given maternity and parental leave in the amount of 730 calendar days. Out of the maternity and parental leaves an employee shall be paid for 183 calendar days in general, whereas in the event of pregnancy complications or multiple birth, 200 calendar days shall be paid.
Can the pregnancy be the reason for dismissal?
Pregnancy is not a reason for the dismissal of an employee. According to article 37, (3) (C) of the Georgian Labor Code – Labour relations shall in no event be terminated during the maternity and parental leave, newborn adoption leave, and any additional parental leave.
According to Article 111 (2) of the Law of Georgia on Civil Service, “A civil servant (a woman) may not be dismissed from the service due to staff reduction, long-term incapacity or health condition, as well as the results of Certification during pregnancy or for up to three years during the child-raising period.”
According to Article 8 (2) of the European Social Charter “with a view to ensuring the effective exercise of the right of employed women to protection, the Contracting Parties undertake to consider it as unlawful for an employer to give a woman notice of dismissal during her absence on maternity leave or to give her notice of dismissal at such a time that the notice would expire during such absence.”
Does man have right for paternity leave?
Parental leave can be used by other family members, according to the Georgian Labor Code, the father has the right to paternity leave.
What are the trade unions?
The trade union represents workers' associations (there are also employers' associations) and its main objective is to represent the employees' interests to the employers. To create and to join trade unions is a basic human right, in the fight for better working conditions; In addition, trade unions have a key role in creating social movements and in implementing changes.
What is overtime work?
According to the Georgian Labor Code “overtime work shall be deemed the work performed by an employee under agreement between the parties in the period of time, the duration for which exceeds 40 hours a week for an adult, 36 hours a week for a minor between the ages of 16 and 18, and 24 hours a week for a minor between the ages of 14 and 16.” (Article 17 (3) )
Overtime work shall be paid in an increased amount of the hourly rate of pay. Conditions for overtime work shall be determined by agreement of the parties.
Which documents regulate gender discrimination at workplace?
National legislation related to gender equality at workplace
1. The Labor Code of Georgia
2. The Law of Georgia on Civil Service
3. The Law of Georgia on Gender Equality
4. The Law of Georgia on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination
International level:
1. The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW);
2. Covenant on Civil and Political Rights;
3. The European Convention on Human Rights;
4. ILO Conventions N111, N100;